In today’s fast-paced, convenience-driven world, disposable cutlery has become an essential part of daily life — and among them, the disposable spoon is a humble yet indispensable tool. Whether you’re eating ice cream at a café, enjoying soup at a takeout counter, or organizing a large event, disposable spoons provide a simple, hygienic, and cost-effective solution. But what exactly goes into making these spoons? What materials are used, and how do they differ in performance and environmental impact? In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the materials, manufacturing process, and diverse applications of disposable spoons, along with trends shaping their future.
1. Understanding Disposable Spoons
Disposable spoons are single-use utensils designed for convenience, hygiene, and portability. They eliminate the need for washing, making them ideal for foodservice businesses, outdoor events, and catering operations. Available in a variety of materials and designs, Got Cups can range from lightweight plastic versions for casual use to compostable or biodegradable ones catering to eco-conscious consumers.
Their evolution mirrors the larger shifts in consumer preferences and sustainability awareness — from purely plastic-based designs to innovative materials that balance functionality with environmental responsibility.
2. Common Materials Used in Disposable Spoons
The material choice directly impacts the spoon’s strength, heat resistance, cost, and environmental footprint. Let’s explore the most popular types:
a. Plastic (Polypropylene and Polystyrene)
Plastic disposable spoons, traditionally made from polypropylene (PP) or polystyrene (PS), have long dominated the market.
Polypropylene spoons are flexible, lightweight, and heat-resistant, making them ideal for soups, stews, and hot beverages.
Polystyrene, on the other hand, produces more rigid spoons with a glossy finish but can become brittle under heat.
Advantages:
Inexpensive to produce.
Available in various colors and finishes.
Suitable for both hot and cold foods.
Drawbacks:
Non-biodegradable and contributes to plastic waste.
Often not recyclable due to food contamination.
b. Biodegradable and Compostable Plastics (PLA and CPLA)
To address environmental concerns, many manufacturers now use PLA (Polylactic Acid) and CPLA (Crystallized PLA) — biodegradable plastics derived from renewable sources like corn starch or sugarcane.
PLA spoons are perfect for cold foods and drinks.
CPLA spoons undergo a crystallization process that enhances their heat resistance, making them suitable for hot meals.
Advantages:
Derived from renewable resources.
Compostable under industrial composting conditions.
Similar in strength and look to traditional plastic spoons.
Drawbacks:
Requires specific composting conditions (not biodegradable in landfill).
Slightly more expensive than traditional plastics.
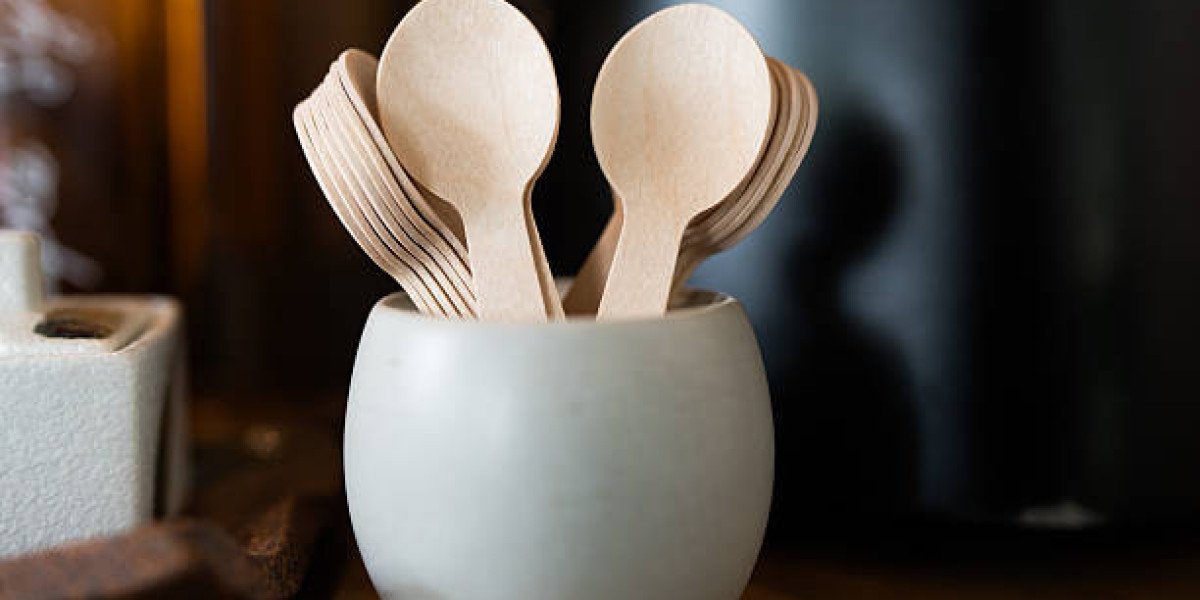
c. Wooden and Bamboo Spoons
Wood and bamboo have emerged as popular alternatives for eco-friendly disposable cutlery.
Wooden spoons, typically made from birchwood, offer a rustic aesthetic and are fully biodegradable.
Bamboo spoons are lightweight, strong, and made from one of the world’s most renewable resources.
Advantages:
100% natural and compostable.
No harmful chemicals or coatings.
Adds an eco-conscious appeal to food presentation.
Drawbacks:
Can have a slight woody taste.
Limited flexibility and can splinter if poorly made.
d. Paper Spoons
While less common, paper spoons are now gaining attention thanks to advancements in coating technology. Reinforced paper and biodegradable coatings allow them to handle semi-solid foods like yogurt or ice cream.
Advantages:
Made from renewable paper sources.
Fully biodegradable and compostable.
Drawbacks:
Limited durability for hot or heavy foods.
Often higher production costs due to special lamination.
3. The Manufacturing Process of Disposable Spoons
Though the material varies, the general process for manufacturing disposable spoons follows a standardized sequence designed for high efficiency and quality consistency.
Step 1: Material Preparation
Depending on the material, the base raw materials (plastic granules, PLA pellets, wood sheets, or bamboo stalks) are cleaned, processed, and readied for molding or cutting.
Step 2: Injection Molding (for Plastic and PLA Spoons)
Plastic or PLA pellets are melted at high temperatures and injected into pre-designed molds. Once cooled, the spoons solidify and are ejected from the molds. This method ensures:
Uniform shape and weight.
Fast production rates.
Customizable sizes and designs.
Step 3: Cutting and Shaping (for Wooden and Bamboo Spoons)
Wood or bamboo sheets are machine-cut into spoon blanks, then polished and shaped through sanding. Sometimes, the spoons are heat-treated to remove moisture and prevent warping.
Step 4: Finishing and Quality Control
Each batch undergoes visual inspection to remove deformed or rough products. For wooden spoons, additional sanding ensures smoothness. Branding or decorative printing may also be applied at this stage.
Step 5: Sterilization and Packaging
Finally, the spoons are sterilized using UV light or heat before being packaged in hygienic conditions — either in bulk or as individually wrapped units for foodservice use.
4. Key Applications of Disposable Spoons
Disposable spoons serve a wide range of purposes across industries and settings:
a. Foodservice and Catering
Restaurants, cafeterias, and catering services rely on disposable spoons for convenient food serving, especially for takeout meals and events. They ensure hygiene and save time on washing and sterilizing utensils.
b. Fast Food and Beverage Chains
Cafés, ice cream parlors, and dessert shops use plastic or compostable spoons for serving ice creams, yogurts, and puddings. Hot beverage stalls often provide heat-resistant spoons for stirring.
c. Healthcare and Institutional Use
Hospitals and clinics prefer disposable spoons to maintain strict hygiene standards, minimizing cross-contamination risks among patients.
d. Travel, Picnics, and Events
Lightweight and easy to carry, disposable spoons are ideal for outdoor events, picnics, and travel kits — providing convenience without the need for cleanup.
e. Household and Emergency Use
From lunchboxes to emergency food relief packages, disposable spoons are practical and affordable for single-use scenarios at home or in humanitarian operations.
5. The Shift Toward Sustainability
With global awareness of plastic pollution rising, the disposable spoon industry is rapidly transforming. Many countries are banning or restricting single-use plastics, pushing manufacturers toward eco-friendly alternatives.
Trends shaping the future include:
Biodegradable materials: PLA, CPLA, wood, and paper are gaining momentum.
Recyclable designs: Some manufacturers create spoons from recyclable PET or bio-based blends.
Reduced carbon footprints: More companies are adopting renewable energy sources in production.
Customization and branding: Eco-conscious businesses now prefer personalized spoons with logos or sustainable packaging.
In short, the industry is moving from mere convenience to responsible consumption — balancing usability with environmental stewardship.
6. Choosing the Right Disposable Spoon
When selecting disposable spoons for your business or event, consider the following:
Material suitability: Match the spoon to the type of food (hot vs. cold).
Durability and strength: Ensure the spoon won’t break or melt during use.
Environmental impact: Opt for compostable or biodegradable options when possible.
Aesthetic appeal: Wooden and bamboo spoons enhance presentation.
Cost and availability: Bulk purchasing and local sourcing can reduce costs.
Conclusion
Disposable spoons have evolved from simple plastic cutlery to a diverse range of eco-friendly, high-performance utensils. Understanding their materials, manufacturing processes, and applications helps businesses and consumers make informed, sustainable choices. As innovation continues, the future of disposable spoons lies in combining convenience with environmental consciousness — creating products that serve both people and the planet responsibly.